What is RDF ?
Due to changing environmental legislation and the need for alternative fuels, new designs for mechanical and biological treatment of solid waste are being developed. The Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF) process is an alternative fuel production process by shredding, sorting and dehydrating the light fraction of the Municipal Solid Waste (MSW). The objective of this concept is to obtain high calorific and stable material. These fuels can replace fossil fuels in many applications, such as power or cement kiln plants. Refuse-derived fuel (RDF) is a fuel produced by shredding municipal solid waste (MSW). Once the non-combustible materials such as glass and metals are removed the RDF material consists largely of organic, plastic and biodegradable waste. the RDF can be used in a variety of ways to produce electricity. It can be used alongside traditional sources of fuel in coal power plants.
Advantages of RDF production systems are:
-
Possibility of using as fuel only the fractions with higher calorific value, so to produce a RDF of "quality" comparable to the specifications outlined in the UNI 9903-1
-
Getting a “stabilized” RDF, that for shape and density can be temporarily stored, allowing more flexibility in the management of production operations and in the conveyance of the product. This "unties" the value of RDF by the in the short term needs of users, enabling to defer the conveyance according to market demands
-
Recovering of some valuable materials for recycling
-
Limiting landfill only to fractions or unsuitable material recovery or energy recovery, with reduced volumes from the preliminary grinding
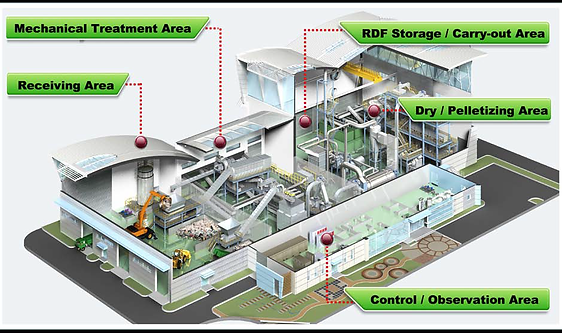
Our Process
We process the domestic wastes to reduce its moisture and separate the metallic and non metallic components from the dry fraction.
The waste material is screened, before being shred, to remove the recyclable parts (e.g. metals), the inert fractions (such as glass) and separate the fine wet putrescible portions (e.g. food and garden waste) containing high moisture and high ash material.
The output of this preliminary process, is then sized, to reach the dimensional specifications according to the normative UNI 9903 -1. The finality of the plant is to stabilize and hygiene the output and to eliminate the residual moisture <25% or < 18% always according to UNI 9903 – 1.
The material is added and mixed then (Blending process) with components with elevate calorific value with the purpose to reach the energetic level required by the end user. These refusals are industrial discards that have constant and precise energetic characteristics notes.
Once the product is ready, the material is then packed in bales in order to optimize its handling and storage.
Please note that the material is constantly analyzed by authorized laboratories that certify that the waste is a special and not dangerous or harmful waste. This is why the material is classified with the CER Code 19 12 10. To this class belong all the wastes that contain mixed material: this refusal is obtained from the mechanical treatment of wastes, not containing dangerous substances (like in CER Code: 19 12 11);The composition of RDF from MSW will vary according to the origin of waste material and the sorting/separation process. This will influence the properties of RDF such as its calorific value.


I'm another title